The concept of 3D-printed food might sound like science fiction, but it’s rapidly becoming a part of our reality. This innovative technology promises to transform our approach to food preparation, offering customization, sustainability, and efficiency. But how exactly is 3D-printed food made? This article delves into the fascinating process behind 3D printed cuisine, exploring the technology, materials, and implications for the future of food.
The Basics of 3D Printed Food
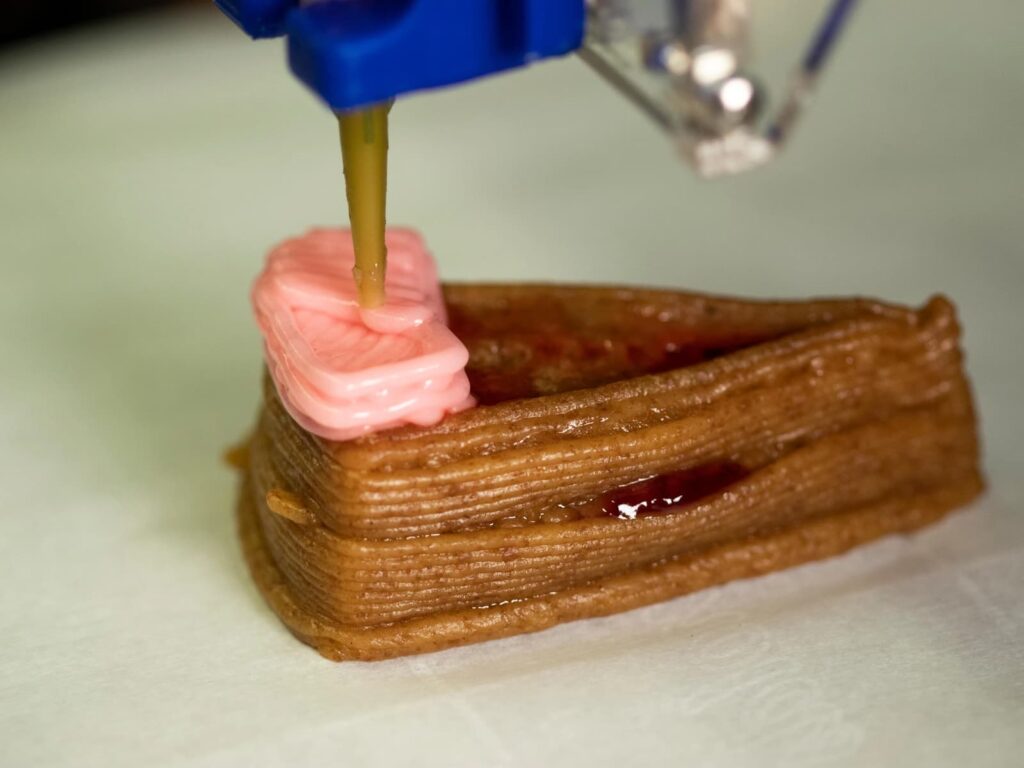
3D-printed food involves a process where edible ingredients are layered and shaped using a 3D printer to create intricate and customized dishes. Unlike traditional cooking methods, 3D printing food offers a level of precision and personalization previously unimaginable, paving the way for a new era in the culinary arts.
Step-by-Step Process
- Design Creation: Initially, a digital 3D model of the desired food item is designed using specialized software;
- Ingredient Preparation: Ingredients must be converted into a printable form, typically purees, pastes, or powders;
- Printing: The 3D printer builds the item layer by layer according to the digital design, using syringes or nozzles to deposit the ingredient precisely;
- Post-Processing: Some printed foods require cooking or additional preparation before consumption.
Ingredients Used in 3D Printing
The versatility of 3D food printing lies in its ability to use a wide range of ingredients, from chocolate and dough to pureed fruits, vegetables, and meats. This flexibility opens up a world of culinary possibilities, enabling the creation of dishes tailored to specific dietary needs and preferences.
Benefits and Challenges
The benefits of 3D-printed food include unparalleled customization, waste reduction, and the ability to cater to specific dietary requirements. However, the technology faces challenges such as limited texture variety, the slow speed of printing complex items, and the high cost of 3D food printers.
Comparing Traditional Cooking and 3D Printing
| Aspect | Traditional Cooking | 3D Printed Food |
|---|---|---|
| Customization | Limited | Highly customizable |
| Speed | Fast for simple dishes | Slower, depending on the complexity |
| Ingredient Diversity | Broad | Depends on printer capability |
| Nutritional Control | General | Precise |
| Waste | Higher | Reduced |
The Future of 3D Printed Food
The potential of 3D-printed food extends beyond novelty, promising innovations in personalized nutrition, sustainable food production, and even space travel. As the technology evolves, it could become a staple in both home kitchens and professional settings, offering exciting possibilities for culinary creativity and dietary management.
Video Guide
To answer all your questions, we have prepared a video for you. Enjoy watching it!
Conclusion
3D-printed food represents a significant leap forward in the way we think about and prepare food. By combining technology and culinary arts, it offers a glimpse into a future where food is more personalized, sustainable, and creative. As technology continues to develop, the possibilities for 3D-printed food are as limitless as the imagination of those who create it.
This exploration into the making of 3D-printed food uncovers the intricacies of a technology set to revolutionize our culinary experiences. With its ability to customize, reduce waste, and open new avenues for food production, 3D-printed food is poised to change our relationship with what we eat, making the future of cuisine as exciting as it is delicious.